HOW DO SEQUENCE BUNDLES WORK?
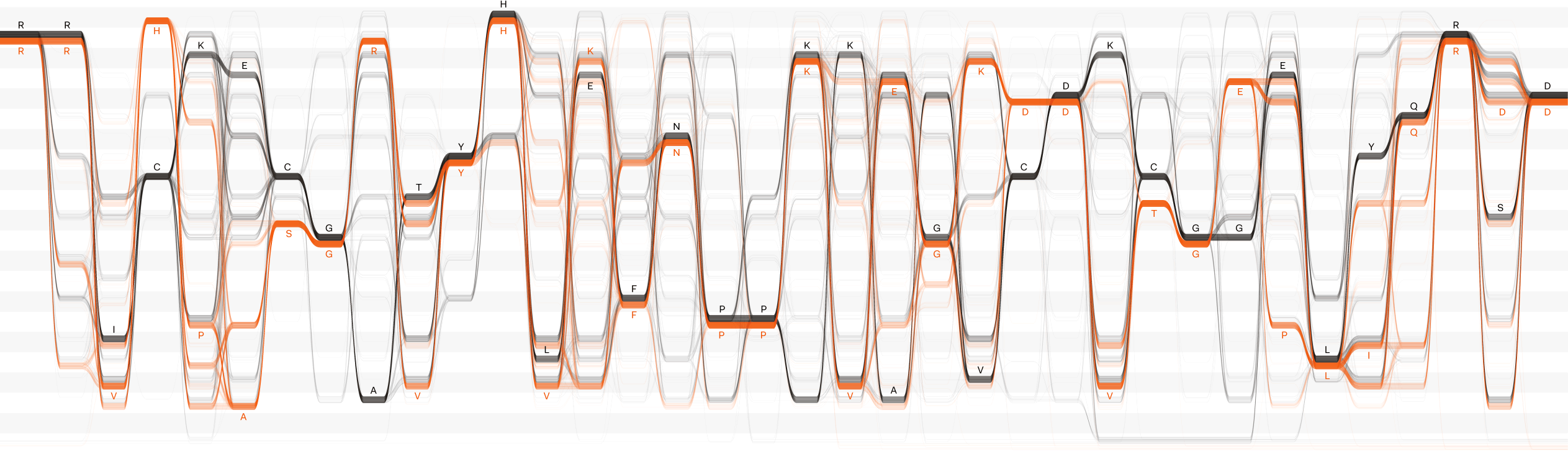
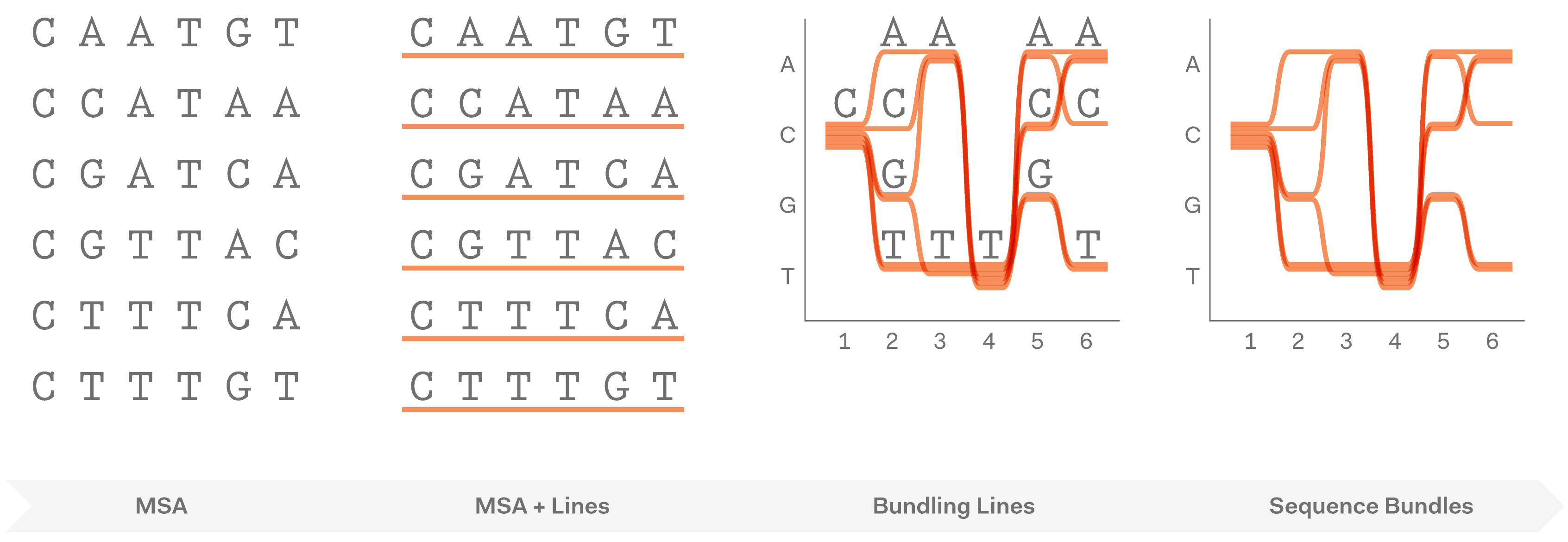
In Sequence Bundles, each sequence from a multiple sequence alignment (MSA) is represented as a single continuous line. At each position in the MSA, these lines are bundled together when they share the same residue. Lines are stacked one on top of another to visualise the entire MSA.
This creates meaningful patterns in the visualisation: lines converge to indicate residue conservation on given positions and diverge to show variation. Continuity of each sequence is preserved, which makes it possible to observe important residue correlations and uncover hidden sequence motifs.
WHAT ARE THEY GOOD FOR?
Sequence Bundles provide a holistic overview of sequence conservation, correlations and motifs in genomic and proteomic data. Well suited for human perception, it allows for intuitive exploration of alignments, gathering of insight and hypothesis generation.
In our article in BMC Proceedings we discuss findings made when using the Sequence Bundles visualisation method.
WHO MADE SEQUENCE BUNDLES?
Sequence Bundles were created by Science Practice.
The Sequence Bundles web-app was developed by Science Practice, with the help of Joe Lau and in collaboration with the Goldman Group at the European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI) in Hinxton, UK. It is kindly hosted on EMBL-EBI servers.
SEQUENCE BUNDLES IN PUBLICATIONS
Publications that discuss, cite or use Sequence Bundles:
-
Sequence Bundles: a novel method for visualising, discovering and exploring sequence motifs. M Kultys, L Nicholas, R Schwarz, N Goldman, J King.
BMC Proceedings 2014, 8 (Suppl 2): S8
-
ALVIS: interactive non-aggregative visualization and explorative analysis of multiple sequence alignments. RF Schwarz, AU Tamuri, M Kultys, J King, J Godwin, AM Florescu, J Schultz and N Goldman.
Nucleic Acids Research (05 May 2016) 44 (8): e77
-
Using Visual Analytics to Support the Integration of Expert Knowledge in the Design of Medical Models, Simulations. PJ Giabbanelli, PJ Jackson.
Procedia Computer Science 2015, Volume 51, pp 755–764
-
Understanding the sequence requirements of protein families: insights from the BioVis 2013 contests. WC Ray, RW Rumpf, B Sullivan, N Callahan, T Magliery, R Machiraju, B Wong, M Krzywinski, CW Bartlett.
BMC Proceedings 2014, 8 (Suppl 2): S1
-
Sequence Bundles. J King, L Nicholas, M Kultys.
Science Practice 2013
CAN I USE SEQUENCE BUNDLES?
You are welcome to use the Sequence bundles web-app and free to generate Sequence Bundles visualisations for your own publications or presentations. If you want to publish images generated using Sequence Bundles, please use the Creative Commons CC BY v4.0 license and cite this publication:
We are always interested to hear how Sequence Bundles are used, so please contact Science Practice by email or Twitter to share your ideas and stories with us.